Prostate cancer is a common type of cancer in men – 13 out of 100 men will be diagnosed with it. In Texas, it is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in men. Prostate cancer is the second most common cause of cancer-related deaths for Texan men.
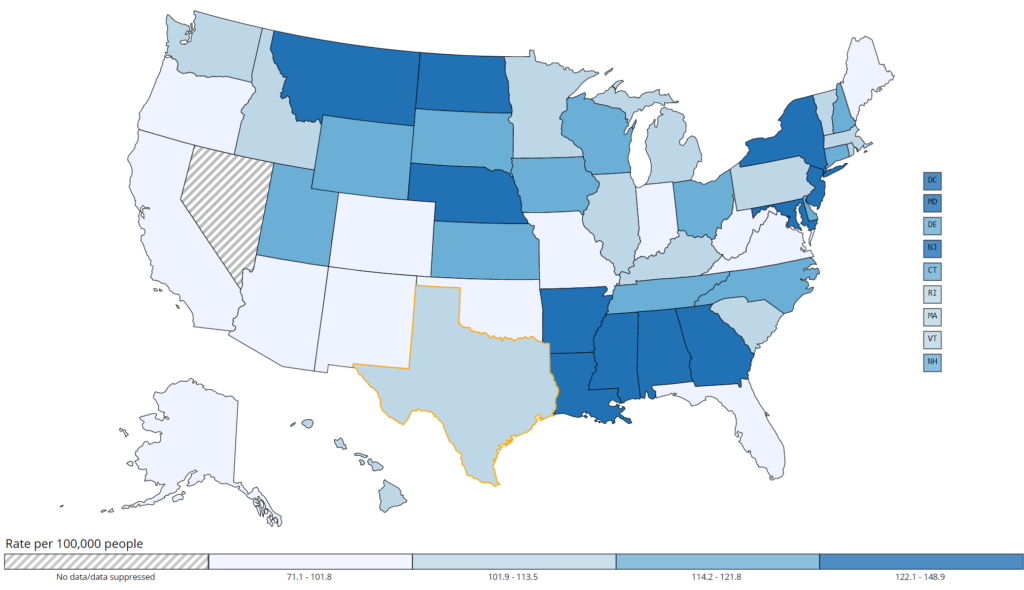
The most common risk factor for prostate cancer is age. Additionally, Black men and those with a family history of prostate cancer are at a higher risk.
Prostate cancer screening is the best defense there is for prostate cancer. Early detection leads to better treatment with fewer side effects. Current screening recommendations are:
- Age 40 – 49: One screening to determine your baseline
- The frequency after that will depend on your doctor’s recommendation based on results and risk factors
- Age 50 – 69: Yearly screening
- Your doctor may recommend a different frequency based on your results and risk factors
- Age 70+: Your doctor will help you determine whether you should continue with screenings
Screening for prostate cancer consists of two tests – a PSA blood test and a digital rectal examination.
- A PSA test is a quick blood test that measures the amount of prostate-specific antigen in your bloodstream. Elevated levels can indicate that you may have prostate cancer and further testing may be recommended.
- A digital rectal examination is a test where a doctor manually feels the prostate through the rectum. The doctor checks for abnormalities of the prostate, which may indicate there is prostate cancer.
Getting screened is a positive step in taking control of your health. Don’t delay and schedule your appointment now.





